The Role of Local NSAID Administration and Inflammation on Tendon Healing
Current clinical treatment following tendon repairs often includes prescribing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce both inflammation and pain. However, some recent studies have shown that NSAID delivery after tendon repair actually impairs healing, noted by reduced collagen production and poor mechanical properties. A few studies have shown improved healing after a delayed delivery of NSAIDs, suggesting that perhaps some early inflammation is necessary to initiate the appropriate wound healing cascade, but that sustained inflammation could be detrimental to tissue remodeling. Therefore, we are interested in investigating the effect of NSAIDs on tendon healing by studying both dose- and time-dependence of local NSAID delivery on rotator cuff tendon repairs using a nanofibrous scaffold drug delivery system.
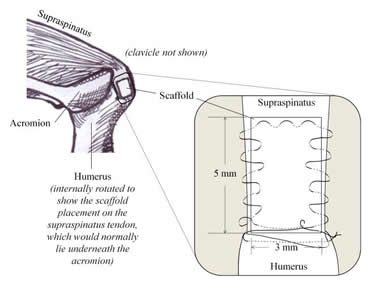 In collaboration with Joseph Bernstein, MD, David Steinberg, MD, Andrew Kuntz, MD, and Robert Mauck, PhD, we have recently received a grant from the Department of Veterans Affairs entitled, “The Role of Local NSAID Administration and Inflammation on Tendon Healing”. In this project, we are first developing a drug delivery system that will provide a defined and well-controlled release of ibuprofen locally to the healing tendon using bilayer delivery system (BiLDS). BiLDS is composed of two electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds with polymeric microspheres of ibuprofen pocketed between the layers. We evaluated this drug delivery scaffold in our clinically relevant rat rotator cuff model of induced overuse injury in conjunction with our supraspinatus tendon repair surgical model to determine the effects of NSAID delivery on tendon healing.
In collaboration with Joseph Bernstein, MD, David Steinberg, MD, Andrew Kuntz, MD, and Robert Mauck, PhD, we have recently received a grant from the Department of Veterans Affairs entitled, “The Role of Local NSAID Administration and Inflammation on Tendon Healing”. In this project, we are first developing a drug delivery system that will provide a defined and well-controlled release of ibuprofen locally to the healing tendon using bilayer delivery system (BiLDS). BiLDS is composed of two electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds with polymeric microspheres of ibuprofen pocketed between the layers. We evaluated this drug delivery scaffold in our clinically relevant rat rotator cuff model of induced overuse injury in conjunction with our supraspinatus tendon repair surgical model to determine the effects of NSAID delivery on tendon healing.
For more information, see:
- Taylor BL, Kim DH, Huegel J, Burkholder S, Weiss S, Nuss C, Raja H, Soslowsky J, Mauck RL, Kuntz AF, Bernstein J. Localized Delivery of Ibuprofen via a Bilayer Delivery System (BiLDS) for Supraspinatus Tendon Healing in a Rat Mode. Journal of Orthopaedic Research (2020) (available online)
- Riggin CN, Qu F, Kim DH, Huegel Jm Steinberg DR, Kuntz A, Soslowsky LJ, Mauck R, Bernstein J. Electrospun PLGA Nanofiber Scaffolds Release Ibuprofen Faster and Degrade Slower After In Vivo Implantation. Annual of Biomedical Engineering 45: 2348-2359 (2017).
- Connizzo BK, Yannascoli SM, Tucker JJ, Caro AC, Riggin CN, Mauck RL, Soslowsky LJ, Steinberg DR, Bernstein J. The Detrimental Effects of Systemic Ibuprofen Delivery on Tendon Healing Are Time-Dependent. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 2013 (In Press).
