Our Research
The lab uses a variety of approaches in a rodent model to further our understanding and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, mood disorders, and addiction.
Example research topics
To examine the role of specific neural pathways in alcohol and drug self-administration, we are using optogenetics in transgenic Long-Evans rats to control neurotransmitter release at specific target areas.
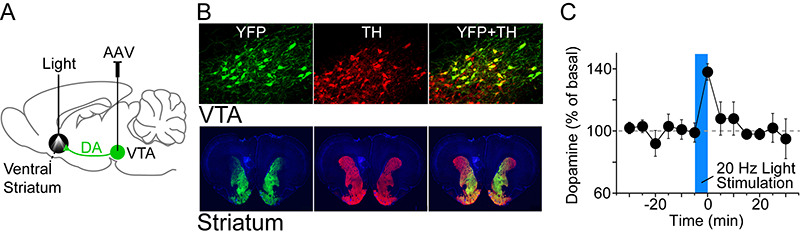
We showed in Thomas et al. (2018) and Ostroumov et al. (2016) that adolescent nicotine or acute stress exposure attenuates alcohol-induced dopamine signals and increases drinking in rodents. Both stress and nicotine cause midbrain circuitry changes via neuroendocrine signals that ultimately impair a chloride transporter and shift GABA inhibition toward excitation.
The role of dopamine in reward signaling is well known, but Broussard et al. (2016) showed that dopamine D1-like receptor activity in the hippocampus is necessary for retention of aversive memories. Our results indicate dopaminergic function within the hippocampus affects long-term synaptic potentiation associated with aversive memory retention.
Commonly used techniques
- Operant drug administration
- In vivo microdialysis and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
- In vivo and slice electrophysiology
- Viral circuit mapping
- Optogenetics
- Behavioral pharmacology
- Immunohistochemistry
