Infectious Disease
Disclaimer: the clinical information on this site is only meant to serve as a reference. Please consult with your team for individual diagnostic and treatment decisions.
In an effort to maintain standardization of antimicrobial regimens and site-specific antimicrobial sensitivities, the treatment section of most of these infections will refer you to the UPHS Antibiotic Stewardship website (under Penn’s DuoMobile authentication) rather than list specific antimicrobial regimens. Please remember to discuss with the floor pharmacist re: patients with renal impairment, hepatic impairment, drug interactions, weight-based dosing, and other patient-specific factors.
COVID-19
UPHS Antibiotic Stewardship Guidelines: For COVID-19
Fever Workup
- Initial workup: peripheral blood cultures x 2, UA/urine culture (if Foley change Foley first), chest Xray, sputum culture (if applicable), respiratory viral panel (if applicable), C.diff (if applicable), examination of wounds and indwelling lines
- First-line differential: pneumonia or influenza, UTI/pyelonephritis, bacteremia, C.diff
- Second-line differential: viral/bacterial gastroenteritis, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, meningitis/encephalitis
- Third-line differential: intra-abdominal abscess, dental abscess, sinusitis, septic arthritis, acute HIV/EBV/CMV, DVT or PE, drug fever, autoimmune condition, malignancy
Neutropenic Fever
- Defined as temperature of 100.4F in a patient who has an ANC (absolute neutrophil count) of 500 or an ANC of 1000 expected to fall (ex: recent chemotherapy). Some sources use an ANC of 1500 as a cutoff.
- Patients form ulcers in areas of high cell turnover (oral/GI mucosa) and are more prone to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and also fungal infections
- Empiric antibiotics should include Pseudomonal coverage (cefepime/Zosyn)
- Treat for infection course or at least until counts reach ANC 500
- Order neutropenic diet and often single room
- UPHS Antibiotic Stewardship Guidelines for Empiric Treatment/Sensitivities
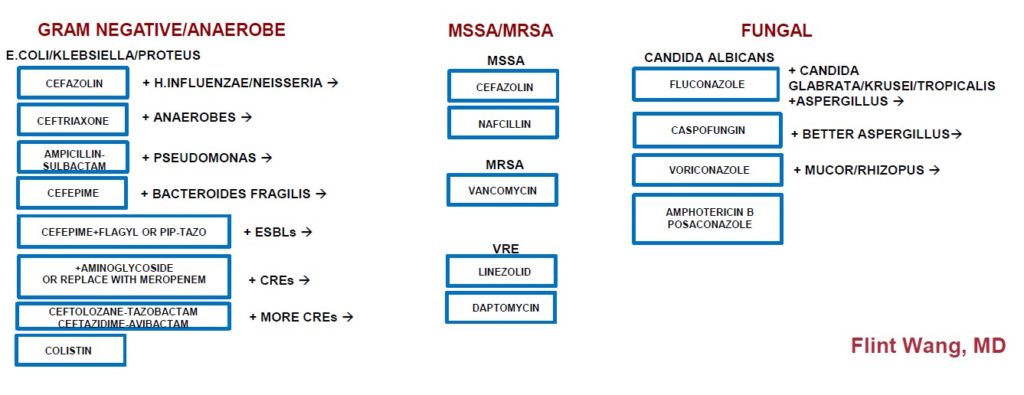
Antimicrobial Escalation: Inpatient
Aspiration Pneumonitis/Aspiration Pneumonia
- Aspiration pneumonitis is a chemical burn from oral/gastric secretions that often has a brief but sharply elevated fever and brief but strikingly CXR infiltrate with respiratory distress that goes away without antibiotics after several hours. Aspiration pneumonia is an infection with neutrophil exudates so the fever, respiratory distress, and CXR infiltrate appear more gradually. Not every aspiration needs antibiotics.
- Aerobic bacteria: Strep pneumoniae, Staph aureus, Haemophilus influenzae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella
- Anaerobic bacteria: Bacteroides, Prevotella, Fusobacterium, Peptostreptococcus
- UPHS Antibiotic Stewardship Guidelines for Empiric Treatment/Sensitivities
C.diff
- Suspect if elevated WBC and/or diarrhea once laxatives have stopped or if recent antibiotics
- If test shows C.diff gene positive but toxin negative, they may be colonized. If immunosuppressed and patient has continued diarrhea may choose to treat
- Treatment regimens can include oral vancomycin, fidoxamicin, and IV Flagyl, now less commonly oral Flagyl
- UPHS Antibiotic Stewardship Guidelines for Empiric Treatment/Sensitivities
Cellulitis
- Bilateral cellulitis is rare
- Non-purulent cellulitis: lower suspicion of MRSA vs purulent cellulitis (generally want to include MRSA coverage)
- Consider monitoring for necrotizing fasciitis or drainage fluid collections
- UPHS Antibiotic Stewardship Guidelines for Empiric Treatment/Sensitivities
Cholangitis
- Cholelithiasis: presence of gallstones, may have biliary colic from intermittent blockage
- Choledocholithiasis: gallstone stuck in bile duct (may affect pancreatic duct)
- Cholecystitis: acute inflammation but not infection of gallbladder due to obstructing stone
- Cholangitis: cholecystitis with inflammation to the point of bacterial ascending infection. Charcot’s triad of cholangitis = fever, jaundice, abdominal pain. Reynold’s pentad of cholangitis: fever, jaundice, abdominal pain, hypotension, altered mental status.
- Based on severity may consider conservative management, antibiotics, cholecystectomy, percutaneous cholecystostomy, MRCP/ERCP/sphincterotomy
- UPHS Antibiotic Stewardship Guidelines for Empiric Treatment/Sensitivities
Influenza
- Tamiflu (oseltamivir) can be used in the first 48 hours of symptoms to reduce influenza symptoms by one day
- Higher risk patients can be treated with Tamiflu even after 48 hours of symptoms
- Dosing is different in transplant patients and CKD/ESRD patients
- UPHS Antibiotic Stewardship Guidelines for Empiric Treatment/Sensitivities
Meningitis/Encephalitis
- Symptoms/signs: fever, neck stiffness, headache, altered mental status, nausea, photophobia, phonophobia, Brudzinski’s sign (flexing the neck causes the hips/knees to flex), Kernig’s sign (hip/knee start flexed, extending the knee causes pain)
- Diagnosis: head imaging (CT or MRI) followed by lumbar puncture (look for positive culture, leukocytosis (neutrophil or lymphocyte predominant), xanthochromia, bleeding, low or normal glucose, high protein)
- Treatment often includes ceftriaxone (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, MSSA), vancomycin (MRSA), ampicillin (Listeria, sometimes reserved just for kids or neutropenic or older adults), acyclovir (HSV)
- UPHS Antibiotic Stewardship Guidelines for Empiric Treatment/Sensitivities
Pneumonia
- Community-acquired pneumonia: UPHS Antibiotic Stewardship Guidelines for Empiric Treatment/Sensitivities
- Healthcare-associated or hospital-acquired pneumonia: consider getting a sputum culture if possible and MRSA nasal swab: UPHS Antibiotic Stewardship Guidelines for Empiric Treatment/Sensitivities
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) and Pyelonephritis
- UA usually with 20-50 WBC and minimal squamous epithelial cells, leukocyte esterase/nitrites may be possible. 10-20 WBC is a gray area. Neutropenic patients may not mount WBC in the urine. Ensure it’s a clean collection and if the patient has a Foley that the Foley is changed before drawing a UA/urine culture. Ideally cultures are collected pre-antibiotics.
- Uncomplicated UTI: no recent antibiotic use or healthcare exposure and not a male.
- Complicated UTI: recent healthcare exposure, catheter-associated, immunosuppressed, recent antibiotic use, urologic anatomic issue, pregnant, or male.
- Pyelonephritis: may have CVA (costovertebral tenderness), may have perinephric stranding on ultrasound/CT, remember kidney transplant patients have their transplanted kidney graft in the lower anterior abdomen so they will have anterior abdominal pain and may have no dysuria due to nerves being cut during the transplant surgery, treatment is based on culture data.
- UPHS Antibiotic Stewardship Guidelines for Empiric Treatment/Sensitivities

