Abnormal Bleeding
Key Conditions
Core 1 (Pre-Clerkship)
- Biomedical Science
- Blood
- Bone Marrow
- MDTI
- Platelets
- Inherited Blleding Diroders
- Acquired Thrombotic Disorders
- Inherited Thrombotic Disorders
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelets
- Intro to Anemia
- Iron deficiency
- DNA metabolism, B12, folate deficiency
- Hemolytic anemia
- Sickle Cell Disease
- Thalassemia
- Core 2 (Clerkships)
- Core 3 (Post-Clerkship)
- Electives that may further knowledge: Pediatric Hematology
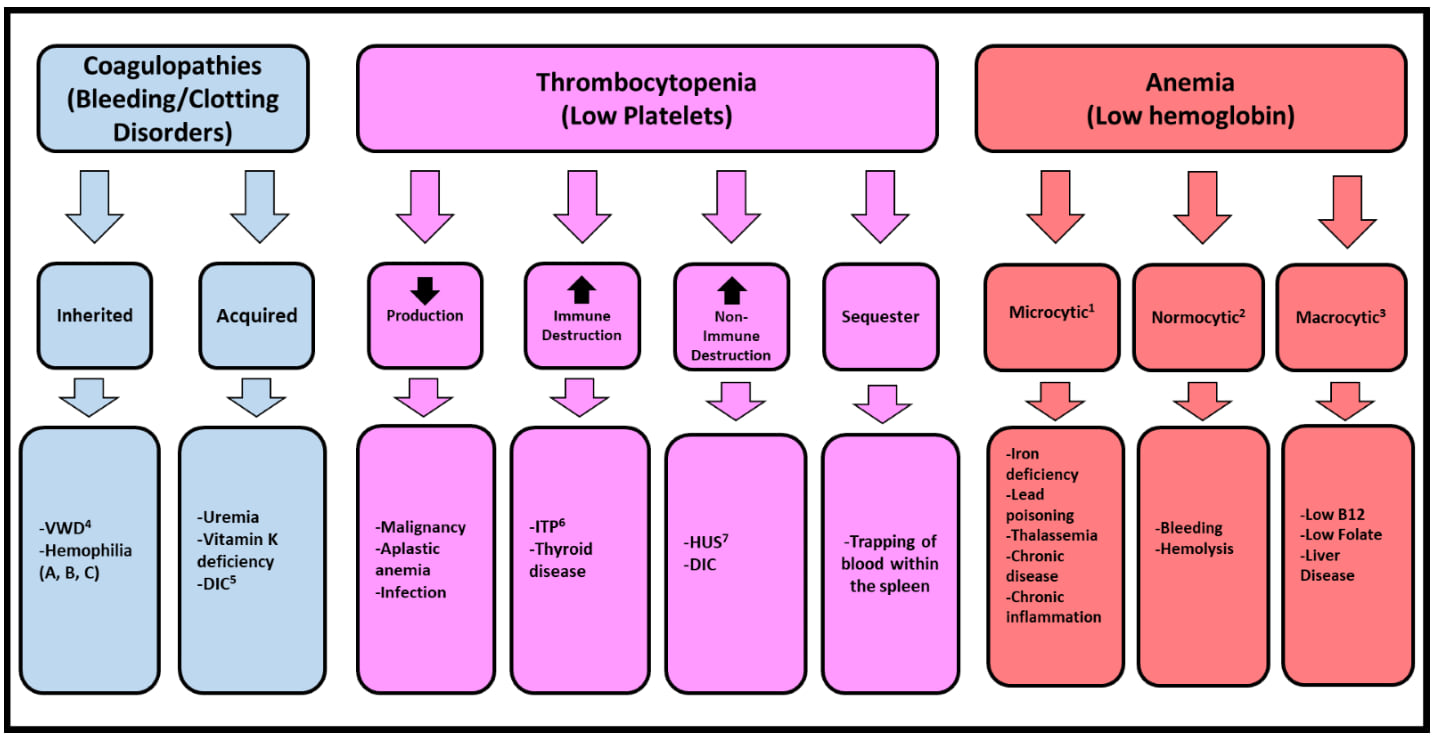
1) Smaller than normal red blood cells 2) Normal sized red blood cells 3) Larger than normal red blood cells 4) Von Willebrand Disease 5) Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation 6) Immune Thrombocytopenia Purpura 7) Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
The chart outlines three hematologic problems—coagulopathies, thrombocytopenia, and anemia—and breaks each into key diagnostic categories such as inherited vs. acquired disorders, platelet production vs. destruction issues, and anemia classified by cell size. Under each category, common causes are listed, including VWD, ITP, HUS, iron deficiency, thalassemia, B12 deficiency, chronic disease, and more.
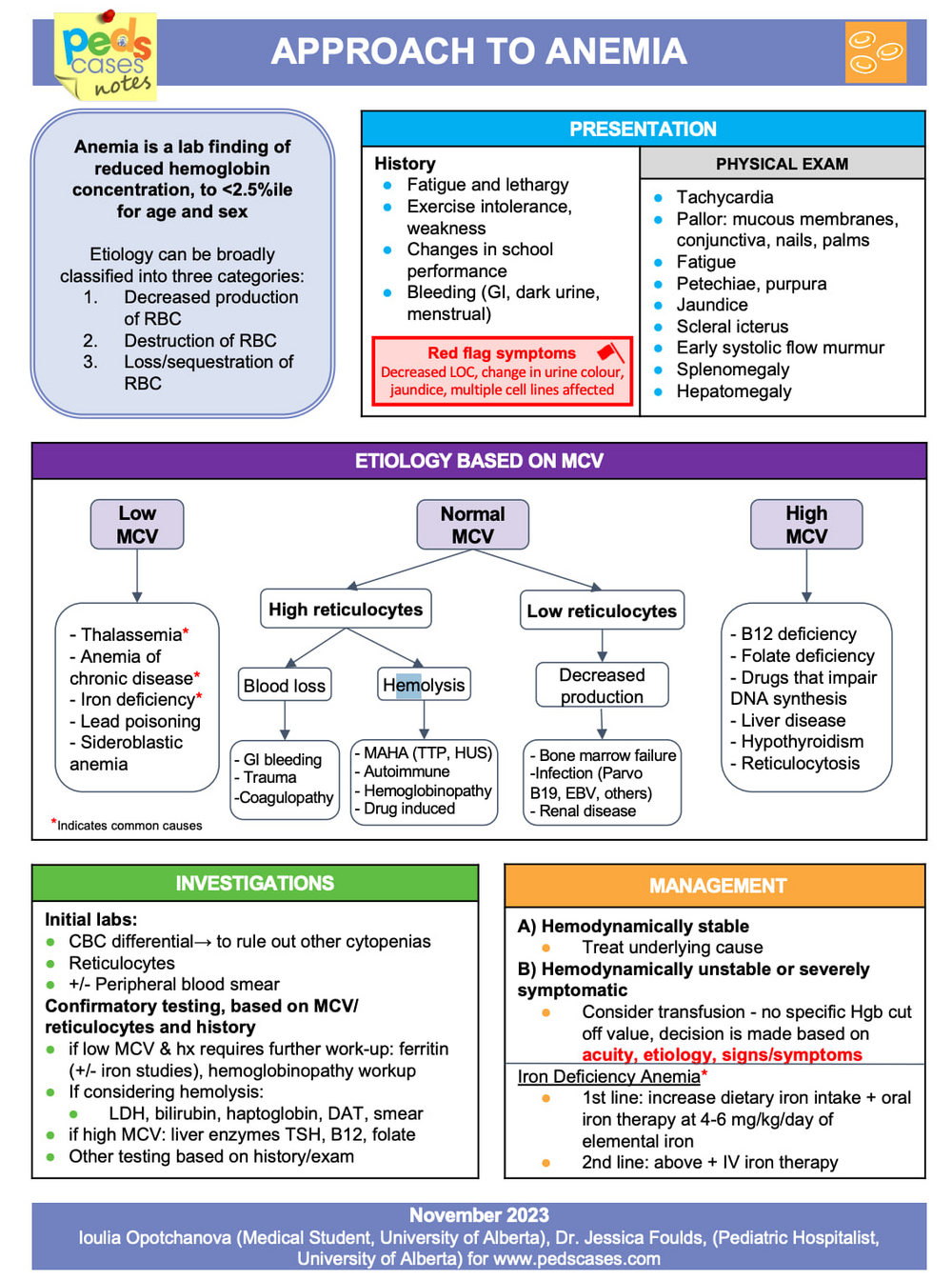
The chart presents an approach to pediatric anemia, starting with common history and physical exam findings and red-flag symptoms. It categorizes anemia by MCV (low, normal, high) and links each category to likely causes such as iron deficiency, hemolysis, blood loss, bone marrow failure, or B12/folate deficiency. It concludes with recommended investigations, confirmatory tests, and management strategies for stable and unstable patients, including specific guidance for iron deficiency anemia.

The chart outlines the presentation of hemolytic anemia in children, including symptoms such as pallor, jaundice, dark urine, fatigue, and splenomegaly. It differentiates intrinsic causes (hemoglobinopathies, membrane defects, enzyme deficiencies) from extrinsic causes (immune hemolysis, MAHA, drug-induced hemolysis) and highlights key investigations and hallmark lab findings like elevated bilirubin, LDH, and reticulocytes with low haptoglobin. Management focuses on treating the underlying cause, supporting hydration, monitoring hemoglobin, and urgently addressing severe anemia or renal failure risk.

The chart outlines how to evaluate thrombocytopenia in children, highlighting important history elements, physical exam findings, and red-flag symptoms that require urgent attention. It summarizes bleeding risk by platelet count, recommended investigations, and major etiologic categories such as immune-mediated destruction (including ITP), consumptive processes like DIC, decreased platelet production, and splenic sequestration. Management considerations for ITP and DIC are also included, emphasizing when observation, corticosteroids, IVIG, or transfusion may be needed.
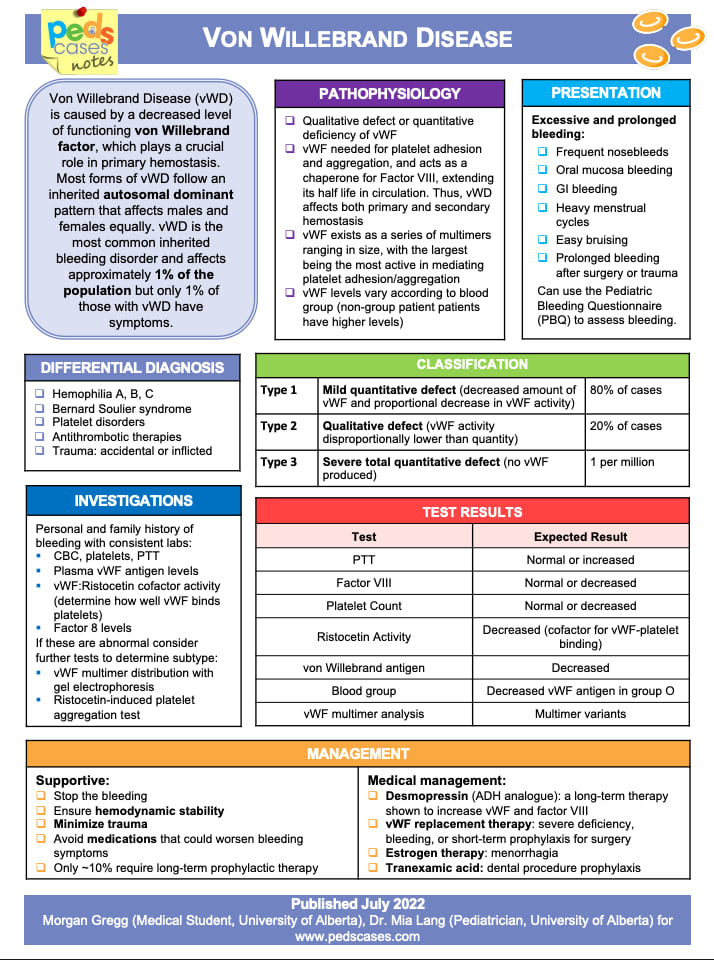
The chart summarizes von Willebrand Disease as an autosomal dominant bleeding disorder caused by quantitative or qualitative defects in von Willebrand factor, leading to mucocutaneous bleeding and prolonged bleeding after injury or procedures. It outlines typical symptoms, diagnostic evaluation—including vWF levels, activity assays, and multimer analysis—and classifies the disease into types 1, 2, and 3 based on severity. Management focuses on supportive care, desmopressin when appropriate, and vWF or Factor VIII replacement for more severe disease or surgical prophylaxis.
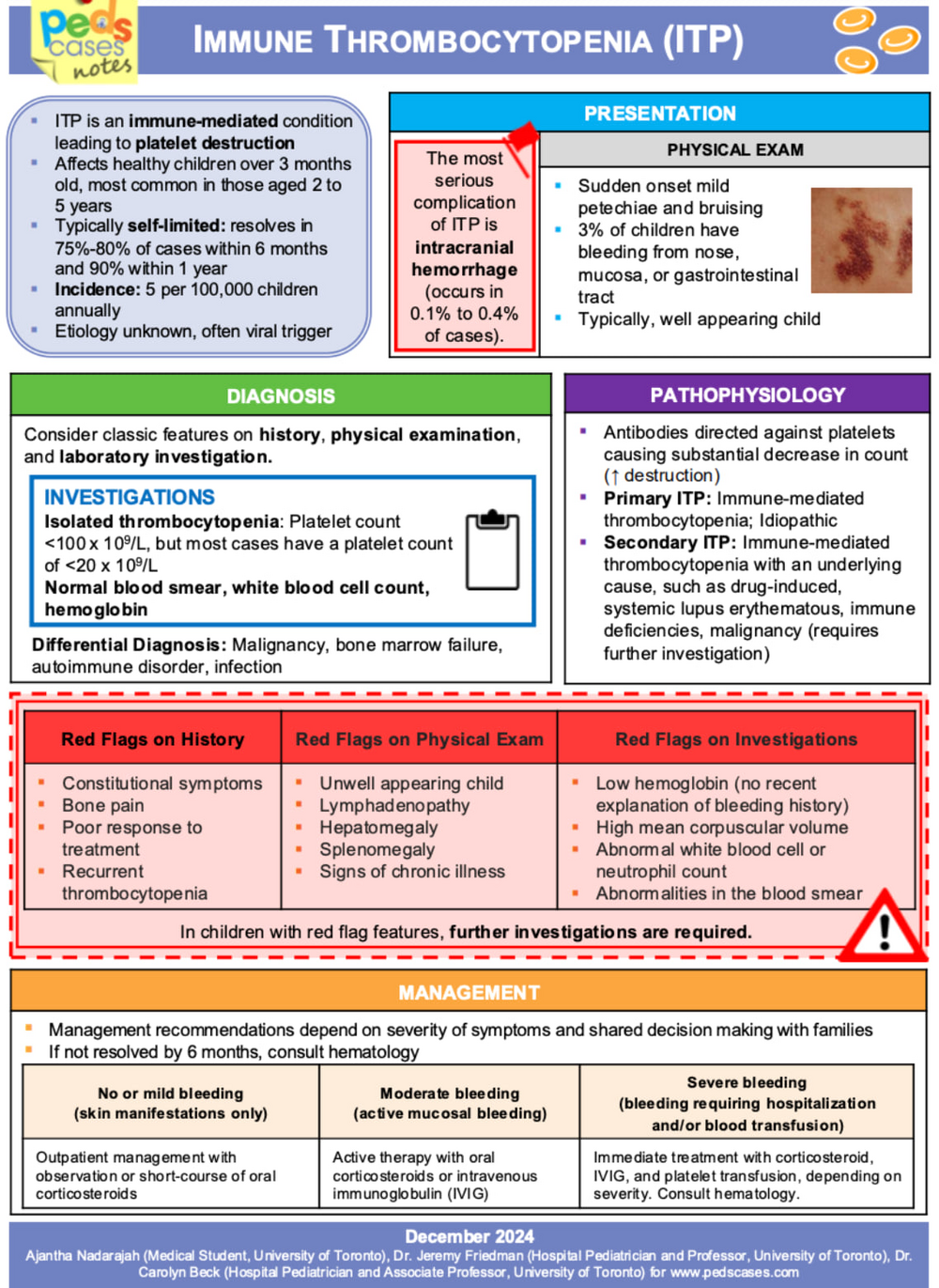
The chart explains ITP as an immune-mediated platelet destruction disorder in otherwise healthy children, outlining typical symptoms such as sudden petechiae and bruising with a normal exam aside from low platelets. It reviews diagnostic features, major red flags requiring further investigation, and the underlying antibody-mediated mechanism distinguishing primary from secondary ITP. Management is guided by bleeding severity, ranging from observation or short-course steroids for mild cases to IVIG, corticosteroids, and possible transfusion for more significant bleeding.
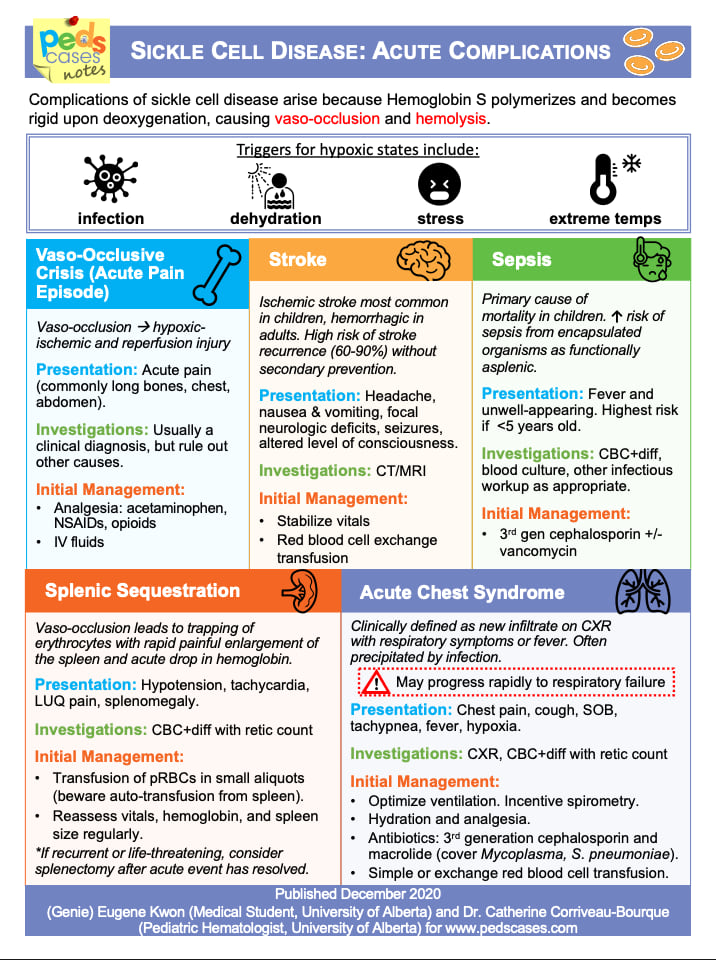
The chart explains that sickle cell complications stem from vaso-occlusion and hemolysis, often triggered by infection, dehydration, stress, or extreme temperatures. It outlines the major acute emergencies—vaso-occlusive crisis, stroke, sepsis, splenic sequestration, and acute chest syndrome—describing hallmark symptoms, essential investigations, and first-line management for each. Acute chest syndrome and splenic sequestration are highlighted as rapidly progressive and life-threatening, requiring urgent recognition and intervention.

