The Genetics of Huntington's Disease
A Basic Overview of the Genetic Process
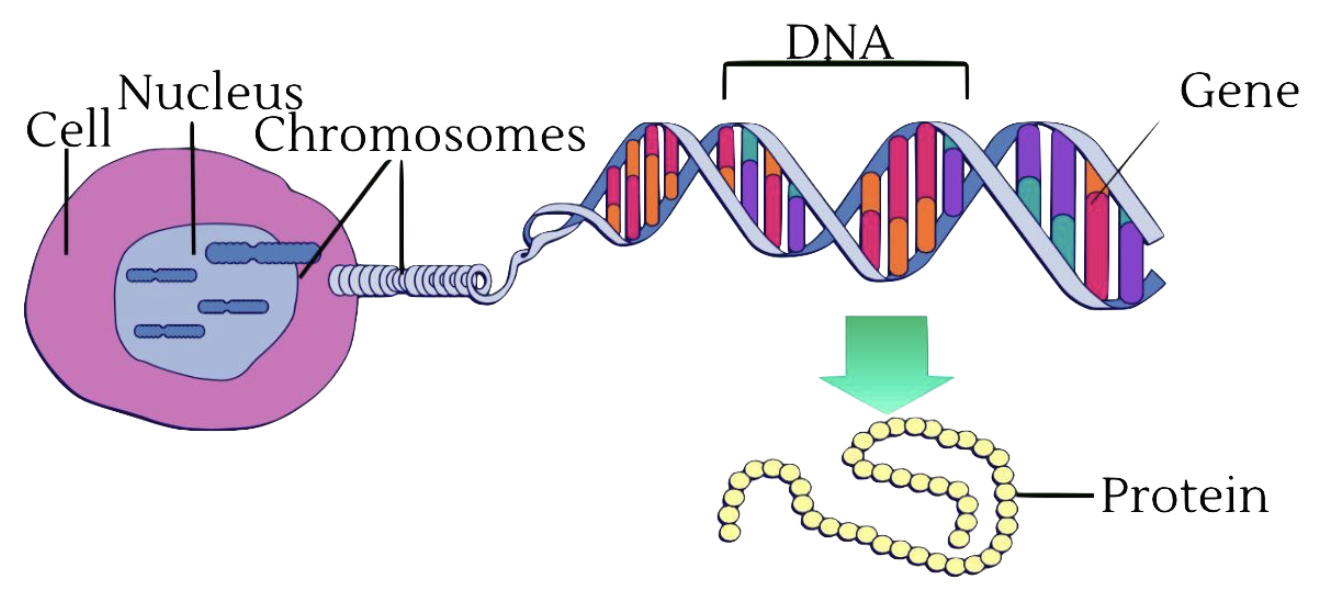
Vocabulary
-
Cells
-
Make up our body
-
-
Chromosomes
-
Each chromosome contains DNA
-
-
DNA
-
The "instruction manual" that tells our cells what to do
-
-
Gene
-
A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a specific protein
-
Huntington's disease (HD) is a genetic disease which means it is passed down through generations. However, up to 10% of people with HD are unaware of or do not have a family history of HD.
The gene responsible for Huntington's Disease is autosomal dominant, therefore, only one copy of the altered gene responsible for CAG repeats is necessary for an individual to have Huntington's Disease.
Each person gets one set of genes from their mother and one set of genes from their father.
The child of an individual with HD has a 50% chance of inheriting the altered HTT gene sequence.
The Specifics of the Genetics of Huntington's
What gene is responsible for HD?
Mutations in the HTT gene are responsible for Huntington's disease. This gene codes for the huntingtin protein and within the HTT gene is a DNA sequence known as the CAG trinucleotide repeat.
What is the relationship between the number of CAG repeats and HD?
Everyone has this sequence but the number of times it is repeated varies. Mutations in the HTT gene affect the number of repeated sequences. There is a range of values that indicate HD status.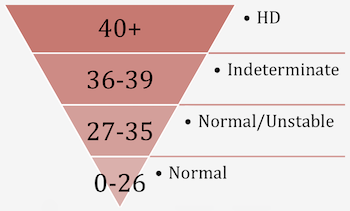
-
A repeat value of 26 or less is considered normal.
-
Values ranging from 27-35 are considered normal but unstable, as the repeat length has the ability to lengthen.
-
While this is not associated with symptoms of HD, an individual with these repeat values has the potential to have a child with a higher repeat length.
-
-
A repeat value of 36-39 places an individual in the indeterminant range.
-
This means an individual may or may not develop HD symptoms.
-
-
Repeat lengths of 40 or above are considered abnormal and indicate the presence of Huntington's disease.

