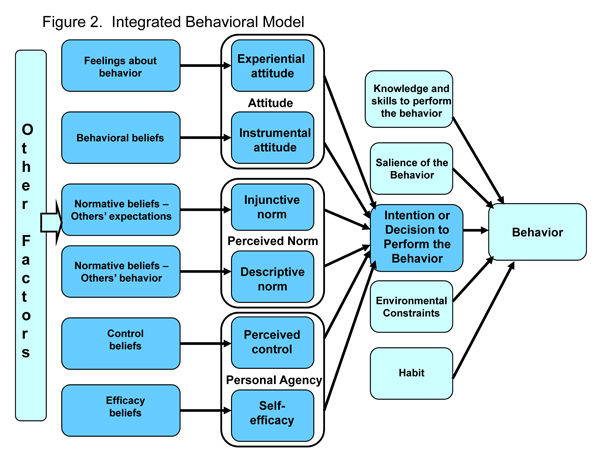
- There are five components that directly affect behavior:
- Similar to TRA / TPB, the most important determinant is intention. Without intention to do so, an individual is unlikely to carry out a behavior. Behavioral intention is determined by attitude, perceived norms, and personal agency (self-efficacy / perceived power).
- An individual needs the knowledge and skills to carry out the behavior.
- The behavior should be salient to the individual (that is, important to the person and at the forefront of their thoughts).
- There should be few or no environmental constraints that make behavioral performance difficult.
- With experience performing the behavior, the behavior will become habitual for the individual.
- Behavior
- Intention or decision to perform the behavior
- Attitude
- Experiential attitude
-Feelings about behavior
- Instrumental attitude
-Behavioral beliefs
- Perceived norm
- Injunctive norm
-Normative beliefs / other's expectations
- Descriptive norm
-Normative beliefs / other's behaviors
- Knowledge and skills to perform a behavior
- Salience of the behavior
- Environmental constraints
- Habit
Integrated Behavioral Model
Constructs
- Intention or decision to perform the behavior
- Definition(s):
- An indication of an individual's readiness or decision to perform the behavior
- The most important predictor a desired behavior will actually occur
- A function of attitudes toward a behavior and perceived norms and personal agency toward that behavior
- Similar to intention in TRA / TPB
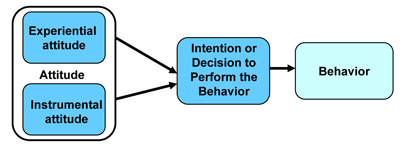
- Attitude, Experiential Attitude, Instrumental Attitude
- Definition(s)
- Attitude refers to an individual's overall perception of favorableness or un-favorableness towards a behavior comprised of affective and cognitive dimensions
- Experiential attitude (or affect) is the individual's emotional response to the idea of performing the behavior
- Instrumental attitude (or cognitive) is determined by beliefs about outcomes of behavior
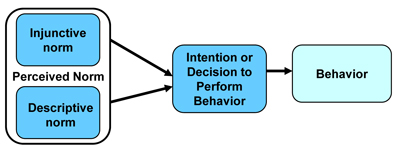
- Perceived norm, Injunctive norm, Descriptive norm
- Definition(s)
- Perceived norm refers to the social pressure one feels to perform or not perform a particular behavior
- Injunctive norm (similar to subjective norm) refers to normative beliefs about what others think one should do and motivation to comply
- Descriptive norm refers to perceptions about what others in one's social or personal networks are doing. Meant to capture situations where there is strong social identity
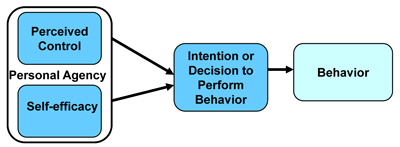
- Personal agency, Perceived control, Self-efficacy
- Definition(s)
- Personal agency refers to individual's capability to originate and direct actions for given purposes.
- Self-efficacy is an individual's belief in his/her effectiveness in performing specific tasks as well as by their actual skill
- Perceived control is an individual's perceived amount of control over behavioral performance. It is determined by control beliefs (an individual's perception of the degree to which various environmental factors make it easy or difficult to perform a behavior)
Similarities in constructs across TRA / TPB, IBM
| TRA / TPB |
IBM |
| Intention to perform a behavior |
Intention or decision to perform a behavior |
Attitude
- Evaluation of behavioral outcomes |
Attitude
- Instrumental attitude |
| Subjective norm |
Injunctive norm |
Perceived control
- Control beliefs |
Perceived control
- Control beliefs |



