Indirect Measurement
- Indirect measurement
- Conduct an elicitation study to elicit commonly held beliefs.
- Develop questionnaire items to assess strength of commonly held beliefs.
- Conduct an elicitation study
- Take a sample of about 25 people from population of study.
- In a focus group or interview setting, use open-ended questions.
- Content analyze the responses into themes. To increase validity, this should be done by two researchers independently. List the themes from most frequently mentioned to least frequently mentioned.
- Develop questionnaire items
- Select the beliefs which are listed most often and convert each of these into a statement.
- Recommended to include about 75% of all beliefs stated.
- Pilot test these items by asking five people from the population of study to answer them and report any difficulty in understanding. If necessary make modifications.
- Scoring
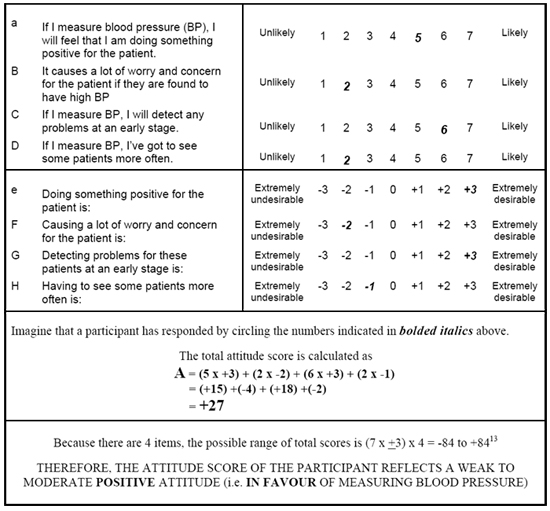
- For each construct measured, the score (i.e. on a 7 point scale, range 1-7) is multiplied by the relevant evaluation score (i.e. on a -3 to +3 scale).
- The resulting products are summed to create an overall construct score.
- Using this method:
- A positive score will indicate an individual is in favor of the behavior.
- A negative score will indicate an individual is against the behavior.
- Sample scoring materials from Francis JJ, Eccles MP, Johnston M, et al. Constructing Questionnaires Based on The Theory of Planned Behavior: A Manual for Health Services Researchers. Centre for Health Services Research: Quality of Life and Management of Living Resources. University of Newcastle: United Kingdom. 2004.
- Behavior: measuring a patient's blood pressure, Construct: attitude
- Sample elicitation study materials from Francis JJ, Eccles MP, Johnston M, et al. Constructing Questionnaires Based on The Theory of Planned Behavior: A Manual for Health Services Researchers. Centre for Health Services Research: Quality of Life and Management of Living Resources. University of Newcastle: United Kingdom. 2004.
- Attitude
- What do you believe are the advantages of X behavior?
- What do you believe are the disadvantages X behavior?
- Is there anything else you associate with your own views about X behavior?
- Subjective Norms
- Are there any individual or groups who would approve of your X behavior?
- Are there any individual or groups who would disapprove of your X behavior?
- Is there anything else you associate with other people's views about X behavior?
- Perceived Behavioral Control
- What factors or circumstances would enable you to X behavior?
- What factors or circumstances would make it difficult or impossible for you to X behavior?
- Are there any other issues that come to mind when you think about X behavior?
